Zambia
June 2023
Latest Updates of Zambia
Projects in Zambia
Projects in Zambia
Our Approach
Agroforestry for Land Management
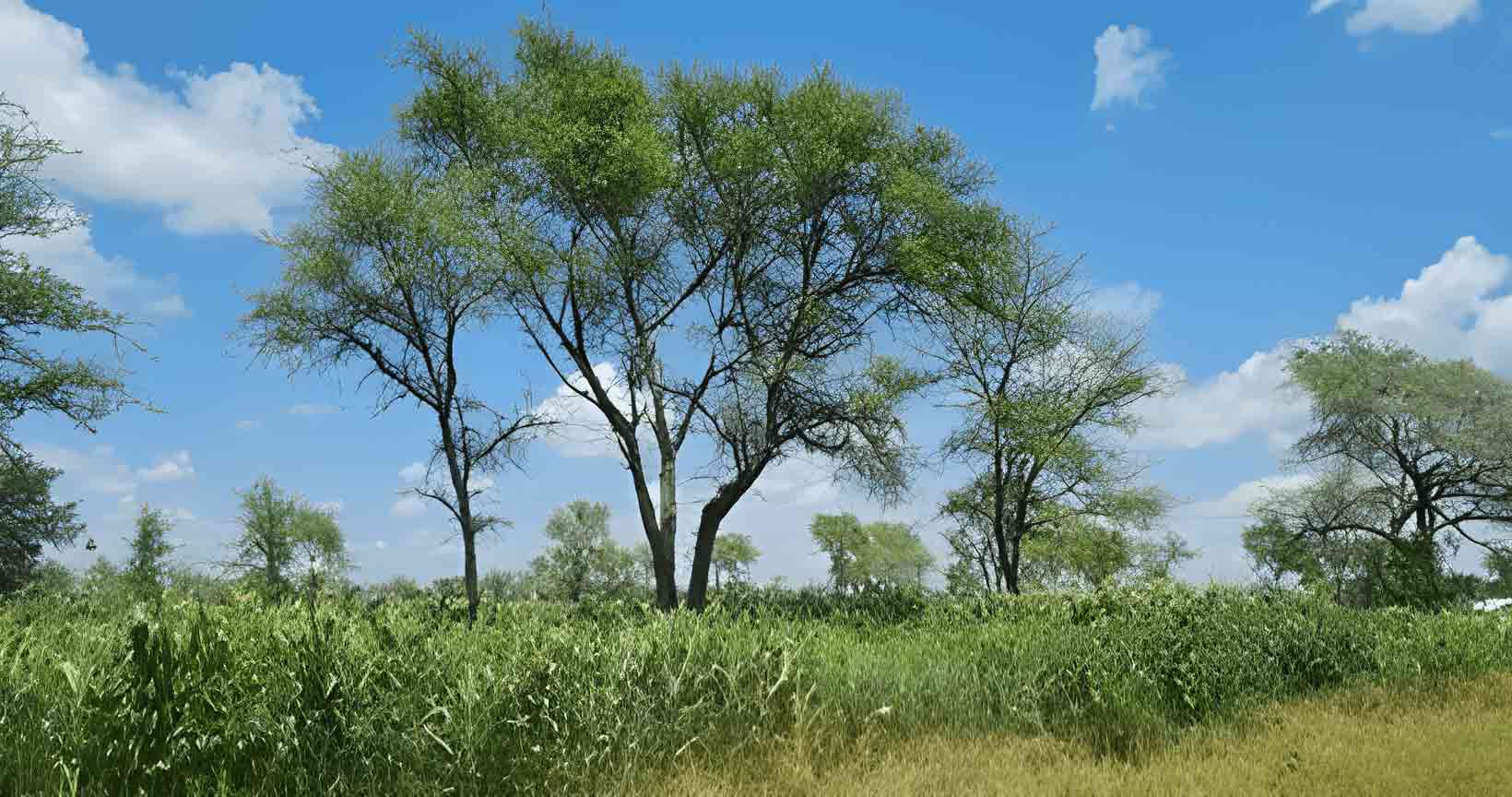
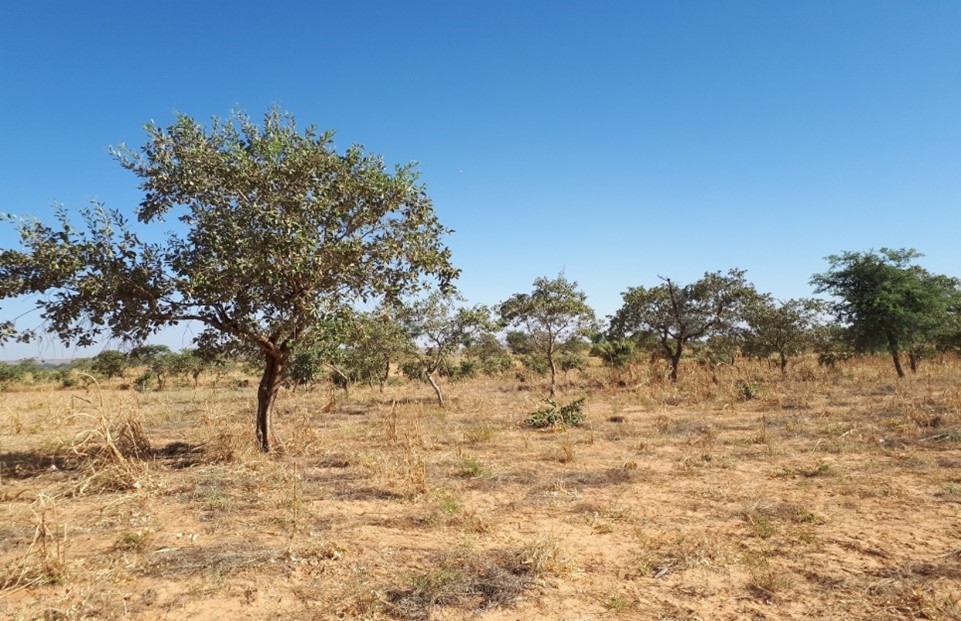
In Zambia, agroforestry promotes sustainable agriculture and forest conservation at the landscape level through sustainable land management to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. Agroforestry raises fast-growing and multipurpose trees in combination with agriculture and livestock. In addition to providing fuel, fodder, wood and other products, trees in agroforestry systems promote water and soil conservation, enhance soil fertility, and acts as wind breaks for nearest crops and other objects.Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR)
Zambia uses the Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR) model in communities to regenerate trees on farmland and forest areas. This helps to improve agricultural productivity and reduce the incidence of droughts, floods, and landslides. FMNR empowers communities who are suffering from the effects of degraded land and climate change. Through FMNR, farmers regenerate trees on their land to improve and increase soil fertility, crops, animal fodder, firewood availability, income, and a better quality of life.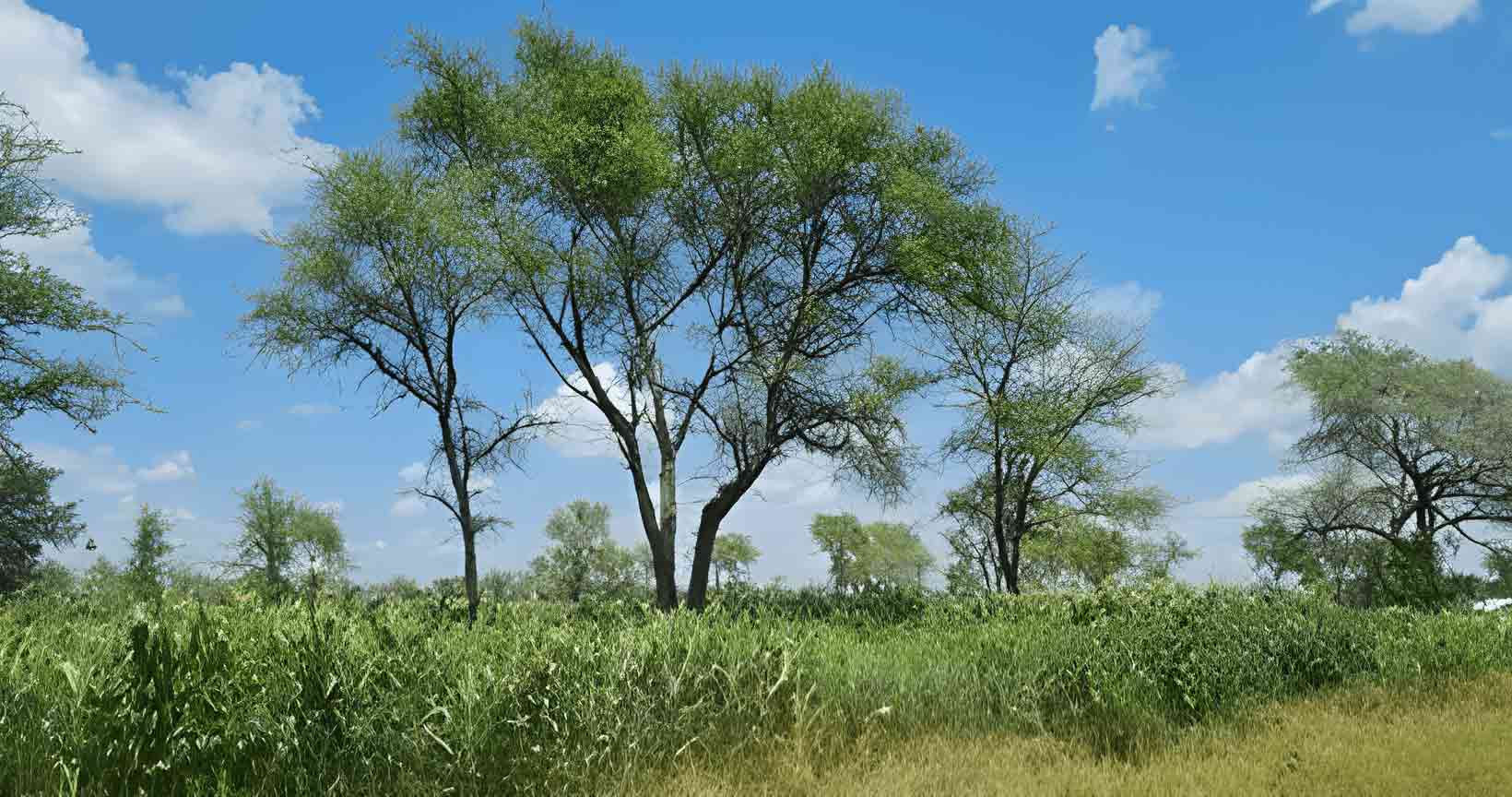
Steps to Success
Stakeholder Involvement
As a party to the UNCCD convention, Zambia has voluntarily set its national land degradation neutrality (LDN) targets and program implementation goals. The country, with the Ministry of Water Development, Sanitation and Environmental Protection as its focal institution, has since embarked on the national target setting process. Because LDN target setting is not a stand-alone process but is embedded in overarching national development policy processes, strong county ownership and the active involvement of all stakeholder groups and sectors impacting the land based natural capital are essential. To involve all relevant stakeholders and achieve land degradation neutrality by 2030, Zambia has formed an LDN working group.
A Coordinating Platform
Zambia established a technical working group (TWG) to improve an inter-departmental and sectoral coordination mechanism. The TWG includes representatives from government, business, academia, research institutions, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
Parnerships
Zambia realizes that the LDN process cannot work in isolation, but that such a concept should be anchored in existing sustainable land management (SLM) efforts being implemented by various stakeholders. In implementing LDN, it is critical to reflect on both the Seventh National Development Plan (7NDP) as a national planning framework and the provisions of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which states that “by 2030 combat desertification, restore degraded land and soil, including land affected by desertification, drought and floods, and try to achieve a land degradation neutrality world”. Zambia has found a strong link between the LDN, SDGs, Zambia’s program and international cooperation in addressing land degradation as well as National and international organizations, NGOs, Civil Society organizations and development partners to achieve Land Degradation Neutrality by 2030.
Key Milestones
- Establishment of national environmental policy

- Launch of Strategic Plan for Lands, Natural Resources and Environmental Protection

- Zambia’s second National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan

- Publication of the Land Degradation Neutrality National Report

- Launch of the national REDD+ strategy

- Zambia committs to restoring 2 million hectares by 2030 with AFR100

Our Vision
Zambia aims to achieve Land Degradation Neutrality (LDN) and restore an additional 5% of national forest cover by 2030.